Another UTI?
Urinary Tract Infections, also known as UTI’s, are considered to be the most common infection, according to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, and are responsible for millions of doctor visits each year.
Because of the female anatomy, namely the small distance between the anus and the vagina as well as the short female urethra (tube that carries urine from the bladder to the external opening, or meatus), women, especially sexually-active women, are highly prone to these infections.
The American College of Medicine predicts at least 50% of women have experienced a UTI in their lifetimes and 1 in 3 women will have had at least 1 episode of UTI requiring antimicrobial therapy by the age of 24 years. Although they are usually nothing to worry about, if left untreated, they could travel up to the ureters (tube that carries urine from kidney to bladder) and eventually infect the kidney causing kidney damage.
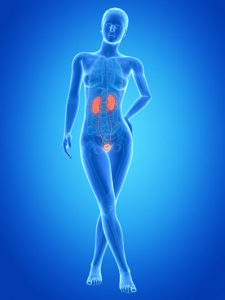
The Urinary System
Urine is produced in the kidney and travels down the ureters and into the bladder for temporary storage until a urinary reflex occurs and we feel the need to urinate. When decide to urinate, the urine travels down the urethra and out through the external opening of the urethra.
UTIs can remain localized in the urethra and bladder or can make their way up to the ureters and kidneys where they become more dangerous.
Signs and symptoms
- Strong urgency to urinate (cannot be delayed)
- Sharp pain or burning during urination
- The urge returns minutes after urination (frequency)
- Urine may have a strong odor
- Urine may look cloudy, could be tinged with blood
- Soreness of the lower abdomen
* If you are experiencing these symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor ASAP to see if antibiotic treatment is needed.
If the infection spreads up to the ureters and the kidneys then symptoms include:
- Back pain
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
** Infection of the kidneys is serious and must be treated with urgency.
Treatment
Currently, the only official treatment for UTI’s is antibiotics. If you feel symptoms of a UTI arising While cranberry juice has been known to disallow bacteria from sticking to the wall of the urethra/ureters, it is not supported by major research and effectiveness is not guaranteed but ACOG guidelines advise that, since there are no negative side effects, you can try this method. The same applies for probiotics which may prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria in the vagina.
** Bacteria feed off of sugar, therefore try and consume unsweetened cranberry juice or cranberry pills rather than cranberry juice cocktail (high glycemic index).
Increased risk for UTI if you:
- Are sexually active
- Are obese
- Are diabetic
- Are pregnant
- Are elderly
- Have had several children
- Have a spinal cord injury and require catheterization to void
- Are with a new partner
- Got your first UTI at a young age
- Are using spermicide
- Are using a diaphragm
- Are menopausal (decrease in estrogen can cause change in vaginal flora that can lead to UTIs)
* recurrent UTI’s
Steps to take towards UTI prevention
- Always urinate immediately before and after sex
- Use other contraceptive methods other than a diaphragm
- Wipe from front to back
- Increase fluid consumption
- Wear cotton underwear
- Refrain from douching
- Take probiotics
- Use vaginal estrogen if postmenopausal (consult with doctor first)
- Empty your bladder every 2-3 hours (as soon as you feel the urge)
